IBM 7010 Simulator Usage
01-Jan-2007
Copyright © 2007, Richard Cornwell
Copyright © 1993-2007, Robert M Supnik
COPYRIGHT NOTICE and LICENSE are at the end of this document.
Contents
- Introduction
- Simulator Files
- IBM 7010 Features
- Stop conditions
- CPU
- I/O Channels (CH1..CH4)
- Unit record devices.
- Magnetic Tape devices
- 7909 Devices
- Symbolic Display and Input
- Character Codes
- COPYRIGHT NOTICE and LICENSE
Introduction
The IBM 1410 and 7010 were designed as enhancements to the IBM 1401, these were somewhat source compatible, but not binary compatible.
The 1410 was introduced on September, 12 1960 and the 7010 in 1962. The 1410 was withdrawn on March 30, 1970.
The 7010 featured 4 I/O channels where the 1410 had 2. Also the 7010 could access 100,000 characters of memory as opposed to the 80,000 for the 1410. The 7010 also featured optional decimal floating point instructions.
Memory was divided into fields separated by a special flag called a word mark. Instructions end at the first character with the word mark set. They consist of a operation code, followed by 1 or 2 5-digit addresses, and an optional instruction modifier.
If the 10’s and 100’s digit have zone bits set the address is modified by the contents of the five characters at locations 25-100.
Each register is 5 characters long and word marks are ignored. The 1410 and 7010 could also be optionally equipped with priority mode to allow for device complete interrupts.
The 7010 or 1410 CPU has no registers. All operations on done from memory.
Simulator Files
To compile the IBM 7010:
| Subdirectory | File | Contains |
|---|---|---|
| I7000 | i7000_defs.h | IBM 7000 simulators general definitions |
| i7010_defs.h | IBM 7010 simulator specific definitions | |
| i7000_chan.c | Generic channel interface. | |
| i7010_cpu.c | 7010 CPU, Channel, interface | |
| I7010_chan.c | 7010 Channel. | |
| i7010_sys.c | 7010 System interface | |
| i7000_cdr.c | 1402 Card reader | |
| i7000_cdp.c | 1402 Card punch | |
| i7000_com.c | 7750 Communications Controller | |
| i7000_con.c | Inquiry console. | |
| i7000_dsk.c | 1301/2302 disk and 7238 drum controller. | |
| i7000_ht.c | 7340 Hypertape controller. | |
| i7000_lpr.c | 1403 Line printer | |
| i7000_mt.c | 729 Tape controller. | |
| i7000_chron.c | Chrono Clock. |
IBM 7010 Features
The IBM 7010 simulator is configured as follows:
| Device Name(s) | Simulates |
|---|---|
| CPU | 7010 CPU with 10-60K of memory |
| CH1..4 | 7010 Channels. |
| MTA | 729 Magnetic Tape Controller (Channel 20) |
| MTB | 729 Magnetic Tape Controller (Channel 21) |
| MTC | 729 Magnetic Tape Controller (Channel 22) |
| CHRON | Chrono Clock |
| CDR | 1402 Card Reader |
| CDP | 1402 Card Punch |
| STKR | 1402 Card Punch Stacker |
| LP | 1403 Line Printer |
| DK | 1301/2302/7304 disk. |
| COM | 7750 communications controller. |
| COML | 7750 Communications lines. |
Stop conditions
The 7010 simulator implements several unique stop conditions:
- I/O Device not ready.
- Unknown CPU instruction
- I/O Check
- Divide Error
- No Word Mark
- Invalid Addresses
- Invalid Instruction Length
- Program Check
- Protection Check
- invalid message to 7750
- No buffer storage available for input character on 7750
- no buffer storage available for output character on 7750
CPU
The CPU options include setting memory size and CPU type.
SET CPU 1401 Emulate a 1401
SET CPU 7010 Emulate a 7010
SET CPU 10K Sets memory to 10K
SET CPU 20K Sets memory to 20K
SET CPU 30K Sets memory to 30K
SET CPU 40K Sets memory to 40K
SET CPU 50K Sets memory to 50K
SET CPU 60K Sets memory to 60K
SET CPU 70K Sets memory to 70K
SET CPU 80K Sets memory to 80K
SET CPU 90K Sets memory to 90K
SET CPU 100K Sets memory to 100K
SET CPU NOPRIORITY No Priority Mode
SET CPU PRIORITY Priority Mode
SET CPU NOFLOAT No Floating Point
SET CPU FLOAT Floating point
SET CPU NOPROT No memory protection
SET CPU PROT Memory Protection
Memory size is 10KW on a standard CPU, extended option must be enabled to use memory sizes over 10KW.
Registers
CPU registers include the visible state of the processor as well as the control registers for the interrupt system.
| Name | Size(digits) | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| IAR | 5 | Instruction Address Register |
| AAR | 5 | A Address Register |
| BAR | 5 | B Address Register |
| CAR | 5 | C Address Register |
| DAR | 5 | D Address Register |
| E | 5 | Channel 0 Address Register |
| F | 5 | Channel 1 Address Register |
| G | 5 | Channel 2 Address Register |
| H | 5 | Channel 3 Address Register |
| ASTRISK | 1 | Asterix Mode |
| SW0..6 | 1 | Sense Switch |
| SW | 6 | Sense Switches. |
The CPU can maintain a history of the most recently executed instructions.
This is controlled by the SET CPU HISTORY and SHOW CPU HISTORY commands:
SET CPU HISTORY clear history buffer
SET CPU HISTORY=0 disable history
SET CPU HISTORY=n enable history, length = n
SHOW CPU HISTORY print CPU history
SHOW CPU HISTORY=n print first n entries of CPU history
The history trace shows the Instruction counter, the AAR and BAR before and after the instruction executed. The result of the instruction is displayed followed by the symbolic instruction.
I/O Channels (CH1..CH4)
The 7010 supported 4 channels.
SET CHAN UREC=dev Sets device to cause interrupts on a channel.
Registers
Channels have the following registers:
| Name | Size(digits) | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| ADDR | 5 | Channel Data Address |
| CMD | 1 | Channel Command. |
| FLAGS | 32 (binary) | Channel Flags |
For meaning of bits in FLAGS see i7000_defs.h.
Unit record devices.
Inquiry Station (INQ)
The inquiry station allows for communications with the operating system.
The station is half duplex and will either print or accept input.
Whenever the computer sends a message it is prefixed with a ‘R’ character.
When the station is ready to receive input it prompts with a ‘I’. Input is buffered until the return character is entered.
Backspace will remove the last character typed.
An <esc> will send an interrupt to the processor to request it read a record from the console.
An <esc> while in input mode will cancel input mode and clear any typed message.
1402 Card Reader (CDR)
The card reader (CDR) reads data from a disk file.
Cards are simulated as ASCII lines with terminating newlines.
Card reader files can either be text (one character per column) or column binary (two characters per column). The file type can be specified with a set command:
SET CDRn FORMAT=TEXT Sets ASCII text mode
SET CDRn FORMAT=BINARY Sets for binary card images
SET CDRn FORMAT=BCD Sets for BCD records.
SET CDRn FORMAT=CBN Sets for column binary BCD records.
SET CDRn FORMAT=AUTO Automatically determines format.
or in the ATTACH command:
ATTACH CDRn <file> Attaches a file
ATTACH CDRn -f <format> <file> Attaches a file with the given format.
ATTACH CDRn -s <file> Added file onto current cards to read.
ATTACH CDRn -e <file> After file is read in, the reader will receive an end of file flag.
The channel can be changed by the following command:
SET CDRn CHAN=c Set this device to channel c
The default assignments are:
CDR0 Channel 1
CDR1 Disabled
The card reader can be booted with:
BOOT CDRn
The CDR Reads first card into address 1 and starts execution at location 1.
Error handling is as follows:
| error | processed as |
|---|---|
| not attached | report error and stop |
| end of file | out of cards |
| OS I/O error | report error and stop |
1402 Card Punch (CDP)
The card reader (CDP) writes data to a disk file. Cards are simulated as ASCII lines with terminating newlines. Card punch files can either be text (one character per column) or column binary (two characters per column). The file type can be specified with a set command:
SET CDPn FORMAT=TEXT Sets ASCII text mode
SET CDPn FORMAT=BINARY Sets for binary card images.
SET CDPn FORMAT=BCD Sets for BCD records.
SET CDPn FORMAT=CBN Sets for column binary BCD records.
SET CDPn FORMAT=AUTO Automatically determines format.
or in the ATTACH command:
ATTACH CDPn <file> Attaches a file
ATTACH CDPn -f <format> <file> Attaches a file with the given format.
The channel can be changed by the following command:
SET CDPn CHAN=c Set this device to channel c.
The default assignments are:
CDP0 Channel 1
CDP1 Disabled|
Error handling is as follows:
| error | processed as |
|---|---|
| not attached | report error and stop |
| OS I/O error | report error and stop |
Stack Device (STKR)
The stacker device can be enabled, and files can be attached to individual bins of the stacker.
The file format follows that of the CDP device.
The individual unit reflects the stacker code sent by the computer.
If no file is attached the output will go to the file attached to the CDP device.
1403 Line Printer (LP)
The line printer (LP) writes data to a disk file as ASCII text with terminating newlines. Currently set to handle standard signals to control paper advance.
SET LPn NO/ECHO Sets echoing to console of line-printer output.
SET LPn CHAN=n Sets channel for this device
SET LPn LINESPERPAGE=lpp Sets number of lines per page on printer.
The default assignments are:
LP0 Channel 1
LP1 Disabled
The printer supports the following control codes to control spacing.
| Character (Octal) | Action |
|---|---|
| 060 | Suppress spacing. |
| 020 | Single space after. |
| 040 | Single space before. |
| 063 | Skip to channel 3 (every 5th line) |
| 062 | Skip to channel 2 (every 8th line) |
| 061 & 069 | Skip to channel 1 (or 9), (top of form). |
Error handling is as follows:
| error | processed as |
|---|---|
| not attached | report error and stop |
| OS I/O error | report error and stop |
Magnetic Tape devices
729 Magnetic Tape (MTA-C)
These come in groups of 10 units each.
Each individual tape drive support several options: MTA used as an example.
SET MTAn REWIND Sets the mag tape to the load point
SET MTAn LOCKED Sets the mag tape to be read only.
SET MTAn WRITEENABLE Sets the mag tape to be writable.
SET MTAn LOW Sets mag tape to low density.
SET MTAn HIGH Sets mag tape to high density.
Options: Density LOW/HIGH does not change format of how tapes are written. And is only for informational purposes only.
Tape drives can be booted with:
BOOT MTxn Read in record into location 0.
ChronoClock
Disabled by default. This is a special 729 tape drive which returns the current time. It supports the option of setting the channel and drive that it will occupy.
Note: You must disable the real 729 drive that is is replacing.
The clock responds to Read and Backspace commands. A read results in a 10 character buffer being generated that has the Month, Day, Hour, Minutes, Seconds and Milliseconds.
This time is taken from the local computer time.
SET CHRON CHAN=n Set channel for chrono clock.
SET CHRON UNIT=n Sets the unit for the chrono clock.
Example: To set Chronoclock to unit A9 do the following:
SET MTA9 DISABLE
SET CHRON UNIT=9 CHAN=1
7909 Devices
These devices must be attached to a 7909 channel to work.
1301/1302/2302/7320 Disk devices
The 7631 file control supports up to ten devices, which can be 7320 drums, 1301 disks, 1302 disks, or 2302 disks. Unit types are specified with the SET command.
SET DKn TYPE=7320 Unit *n* is a drum
SET DKn TYPE=7320-2 Unit *n* is a drum (two modules)
SET DKn TYPE=1301 Unit *n* is a 1301 disk
SET DKn TYPE=130l-2 Unit *n* is a 1301-2 disk (two modules).
SET DKn TYPE=1302 Unit *n* is a 1302 disk
SET DKn TYPE=1302-2 Unit *n* is a 1302-2 disk (two modules).
SET DKn TYPE=2302 Unit *n* is a 2302 disk
Units can be SET ENABLED or DISABLED. In addition, units can be set to enable or disable formatting:
SET DKn FORMAT Enable formatting
SET DKn NOFORMAT Disable formatting
SET DKn HA2 Enable writing of home address 2
SET DKn NOHA2 Disable writing of home address 2
SET DKn MODULE=n Sets modules for unit, modules can only be even. 0 to 8.
SET DKn CHAN=n Sets channel for unit (A-H).
SET DKn SELECT=n Sets select on channel (0 or 1).
SET DKn CTSS Sets disk to use CTSS bootstrap
SET DKn IBSYS Sets disk to use IBSYS bootstrap.
Formatting is disabled by default.
All Disk units support bootstrapping with boot command. Bootstrap code is build based on whether CPU is in CTSS mode or not.
BOOT DKn Insert custom Loader into lower memory and start.
Error handling is as follows:
| error | processed as |
|---|---|
| not attached | report error and stop |
| OS I/O error | report error and stop |
7750 Communications Controller (COM and COML)
The 7750 is modeled as a terminal multiplexer with 33 lines. It consists of two device: COM is the multiplexer controller, and COML is the individual lines.
For the first 32 lines, the 7750 performs input and output through Telnet sessions connected via a user-specified listening port.
The 33rd line is permanently attached to the simulator console window.
The ATTACH command specifies the port to be used for Telnet sessions:
ATTACH COM <port> set up listening port
where port is a decimal number between 1 and 65535 that is not being used other TCP/IP activities.
Each line (each unit of COML) can be set to one of twp modes: KSR-35 and KSR-37. In KSR-35 mode, lower case input and output characters are converted automatically to upper case, and parity is ignored. In KSR-37 mode, lower case characters are left alone, and even parity is generated on input. KSR-37 is the default.
Once COM is attached and the simulator is running, the 7750 listens for connections on the specified port. It assumes that any incoming connection is a Telnet connections. The connections remain open until disconnected either by the Telnet client, a SET COM DISCONNECT command,or a DETACH COM command.
SET COM DISCONNECT=n Disconnect line n
SET COM CHAN=n Set channel for com controller.
The 7750 implements the following special SHOW commands
SHOW COM CONNECTIONS Displays current connections to the 7750
SHOW COM STATISTICS Displays statistics for active connections
The 7750 implements the following special SET commands:
SET COMLn LOG=filename Log output of line n to filename
SET COMLn NOLOG Disable logging and close log file
SET COMLn KSR35 Set line *n* to ksr-35
SET COMLn KSR37 Set line *n* to ksr-37
SET COMLn 2741 Set line *n* to 2741
Registers
The controller (COM) implements these registers:
| Name | Size | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| ENABLE | 1 | Enable flag |
| STATE | 6 | Controller state |
| MSGNUM | 12 | Input message sequence number |
Symbolic Display and Input
The IBM 7010 simulator implements symbolic display and input. These are controlled by the following switches to the EXAMINE and DEPOSIT commands:
-m Display/Enter Symbolic Machine Code
-c Display/Enter BCD Characters
-n Display 1401 Symbolic Machine Code
(none) Display/Enter Octal Characters
The symbolic input/display supports several formats for instruction display:
- <opcode>
- <opcode> <character>
- <opcode> <character><character><character>
- <opcode> <address>
- <opcode> <address>,<address>
- <opcode> <address>,<character>
- <opcode> <address>,<address>,<character>
An address is a decimal number optionally followed by a +Xnn specifying an index register.
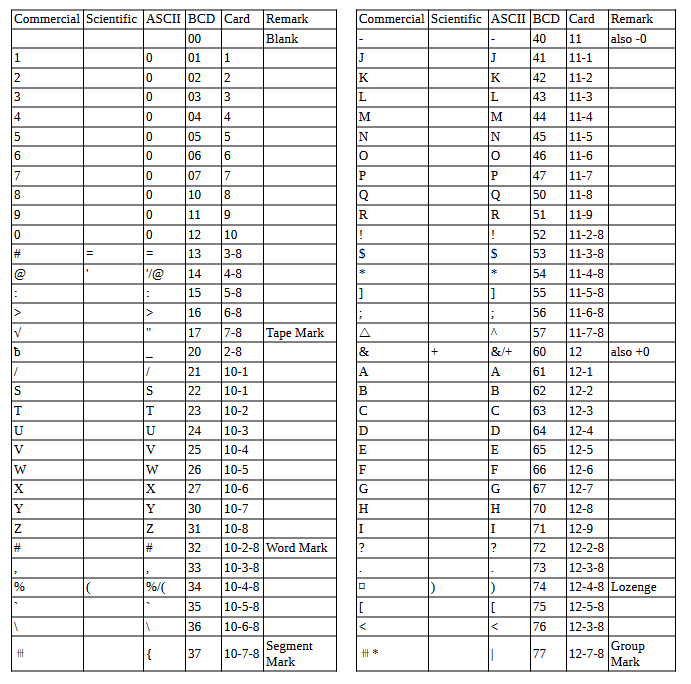
Character Codes
This is the mapping between character codes used by the simulator:
COPYRIGHT NOTICE and LICENSE
The following copyright notice applies to the SIMH source, binary, and documentation:
Original code published in 1993-2007, written by Robert M Supnik
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the “Software”), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS IS”, WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL ROBERT M SUPNIK BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
Except as contained in this notice, the names of the authors shall not be used in advertising or otherwise to promote the sale, use or other dealings in this Software without prior written authorization from each author.